Living with varicoceles can be challenging and overwhelming, especially if you don't know much about the condition. In this blog, we will explore what varicoceles are, their symptoms, causes, and the available treatment options. We will also provide tips on how to manage the discomfort and live a fulfilling life with varicoceles. If you or a loved one is struggling with this condition, this blog will offer helpful insights and practical solutions to help you cope.
What are Varicoceles?
A varicocele is a collection of swollen veins in the scrotum. It is a common condition, occurring in about 15% of young men, and usually causes only minor symptoms. In some men, however, a varicocele is associated with more severe pain which can be troublesome and interfere with normal activities.
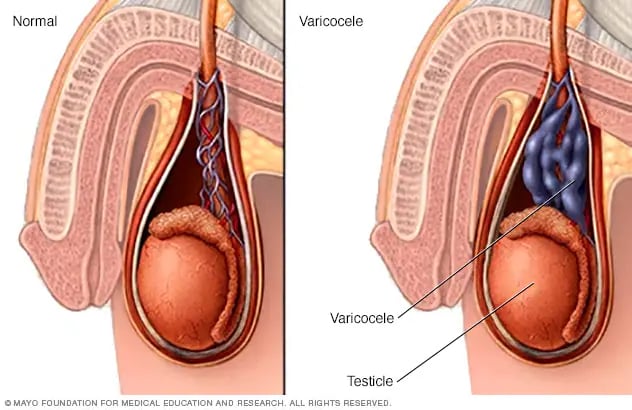
What are the Symptoms of Varicoceles?
A varicocele often produces no signs or symptoms so it can be difficult to know if you have one. Sometimes, you may feel pain or discomfort. Other symptoms include:
- A Dull Ache in the Testicles
- A Feeling of Heaviness in the Testicles
- Visibly Swollen Veins
- Visibly Smaller Testicle
- Infertility
We are often asked, "what does a varicocele look like?" Over time, a varicocele grows and become more noticeable. Varicoceles usually have a 'twisted' appearance (see the above image) and have sometimes been described as looking like a ‘bag of worms’, and the condition might cause a swollen testicle - usually the left side.
Managing Varicoceles
Varicoceles are a common condition that affects the male reproductive system. While varicoceles can often be asymptomatic, some individuals may experience pain, discomfort, or other complications. Treatment for varicoceles typically depends on the severity of the symptoms, the potential impact on fertility, and the individual's overall health. In this context, there are two main categories of treatment options available for varicoceles: conservative and surgical.
Conservative Treatment Options:
Conservative treatment options for varicoceles include lifestyle changes and medications. These options are often recommended for individuals who have mild symptoms or who are not yet ready for surgery.
Lifestyle Changes:
Lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications associated with varicoceles. Some recommended lifestyle changes for individuals with varicoceles include:
- Wearing supportive underwear: Wearing supportive underwear can help reduce pressure on the veins in the scrotum, thereby reducing symptoms.
- Avoiding standing or sitting for long periods: Prolonged standing or sitting can increase pressure on the veins in the scrotum, exacerbating symptoms. Taking regular breaks to move around can help alleviate symptoms.
- Staying physically active: Regular exercise can improve blood flow and reduce inflammation, which can help alleviate symptoms of varicoceles.
- Maintaining a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health, which can help alleviate symptoms of varicoceles.
Medications:
Medications are another conservative treatment option for varicoceles. Medications are typically prescribed to reduce pain and discomfort associated with varicoceles. Some commonly prescribed medications for varicoceles include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with varicoceles.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or nortriptyline, can help reduce pain associated with varicoceles.
While lifestyle changes and medications can help alleviate symptoms of varicoceles, they are generally not considered a permanent solution. Surgical intervention may be necessary for individuals with severe symptoms or for those who are experiencing fertility issues.
Surgical Treatment
Varicocele Embolisation
Varicocele embolisation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat varicoceles. It involves the insertion of a small catheter into a vein in the groin or neck and using imaging guidance to guide the catheter to the affected vein in the scrotum. Once the catheter is in place, a small coil or other embolic material is inserted through the catheter and into the affected vein, blocking the blood flow and causing the vein to collapse. This reduces the size of the varicocele and alleviates symptoms.
Varicocele embolization is typically performed as an outpatient procedure and does not require general anesthesia. It is generally considered to be a safe and effective treatment option for varicoceles, with a success rate of up to 90%. Compared to traditional surgical treatments for varicoceles, such as varicocelectomy, embolization is associated with a shorter recovery time, less pain, and fewer complications.
Varicocele embolization may be recommended for individuals who have failed to respond to conservative treatments or who are experiencing severe symptoms or complications, such as infertility or testicular atrophy. It is also a good option for individuals who wish to avoid the risks and complications associated with traditional surgical treatments.
However, like any medical procedure, varicocele embolization has potential risks and complications. These may include bruising, bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding tissues or organs. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of varicocele embolization with your doctor before undergoing the procedure.
Living with Varicoceles
Like most medical conditions, there are multiple ways to manage your symptoms and the condition itself to improve your quality of life and have as normal a life as possible.
Coping with Physical Symptoms:
Varicoceles can cause a variety of physical symptoms, such as testicular pain, swelling, or discomfort. To manage these symptoms, you can try the following:
- Wearing supportive underwear: Wearing snug-fitting underwear can provide additional support and help alleviate symptoms.
- Applying ice: Applying an ice pack to the affected area can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
Coping with Emotional Impact:
Varicoceles can also have an emotional impact on individuals, especially if they are concerned about the impact on their fertility. To manage these emotions, you can try the following:
- Seeking support from loved ones: Talking to friends and family members about your concerns can help you feel less isolated and more supported.
- Joining a support group: Joining a support group for individuals with varicoceles can provide additional emotional support and the opportunity to connect with others going through similar experiences.
- Seeking professional counseling: If your emotions are interfering with your daily life, it may be helpful to seek professional counseling to learn coping strategies and manage your emotions.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Varicoceles:
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage varicoceles. Some changes you can make include:
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms of varicoceles.
- Avoiding heavy lifting: Heavy lifting can increase pressure on the affected area, exacerbating symptoms. If you have a job or hobby that requires heavy lifting, talk to your doctor about modifying these activities.
- Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help promote overall health and reduce inflammation, which can help alleviate symptoms of varicoceles.
Seeking Medical Attention:
It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of varicoceles. Your doctor can help diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include medications or surgery. If you are concerned about the impact of varicoceles on your fertility, your doctor can also perform tests to evaluate your fertility and make appropriate recommendations.
Overall, living with varicoceles can be challenging, but with the right support and management strategies, it is possible to live a fulfilling and healthy life.
Risks and Complications of Varicoceles
Varicoceles are generally considered to be a benign condition, but in some cases, they can lead to complications that may impact male fertility or result in other health issues. The risks and complications associated with varicoceles can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. In this context, here are some of the most common risks and complications associated with varicoceles:
Impact on male fertility:
Varicoceles are a leading cause of male infertility. The increased blood flow and pressure in the affected veins can lead to an increase in scrotal temperature, which can affect sperm production and quality. This can lead to reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology, all of which can impact male fertility. In some cases, varicoceles may also cause sperm DNA damage, which can further reduce the chances of conception.
Risk of testicular atrophy:
In severe cases, varicoceles can cause testicular atrophy, which is the shrinking of the affected testicle. This occurs due to reduced blood flow to the testicle, which can lead to tissue damage and scarring. Testicular atrophy can lead to a reduction in testosterone production and can further impact fertility.
Other potential complications:
Other potential complications associated with varicoceles may include:
- Pain and discomfort: Varicoceles can cause pain, discomfort, or a heavy feeling in the scrotum. This pain may worsen during prolonged standing or physical activity.
- Cosmetic concerns: In some cases, varicoceles may be visible or palpable through the scrotal skin, causing cosmetic concerns.
- Blood clots: Varicoceles may increase the risk of blood clots, particularly in individuals who are already at risk due to underlying health conditions.
- Recurrence: While surgery or embolization can effectively treat varicoceles, there is a small risk of recurrence.
In Summary
Varicoceles are a common condition that affects a significant number of men, and while they are generally considered to be benign, they can lead to complications that can impact fertility and overall health. Seeking medical attention for varicoceles is essential, as it can help to identify and manage any potential risks or complications associated with the condition.
If you are experiencing symptoms such as pain, discomfort, or swelling in the scrotum, or if you are concerned about your fertility, it is important to talk to your doctor. Your doctor may recommend diagnostic tests such as a scrotal ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the varicocele.
If you have been diagnosed with a varicocele, there are a variety of treatment options available, ranging from conservative measures such as lifestyle changes and medication to more invasive procedures such as surgery or embolisation. It is important to explore all available treatment options and work with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
In conclusion, while varicoceles may not always cause symptoms or complications, seeking medical attention and exploring treatment options can help to prevent potential risks and improve overall health and fertility outcomes. If you are experiencing symptoms or are concerned about your fertility, do not hesitate to book a consultation with Northern Beaches Interventional Radiology to discuss your diagnosis and treatment plan.




